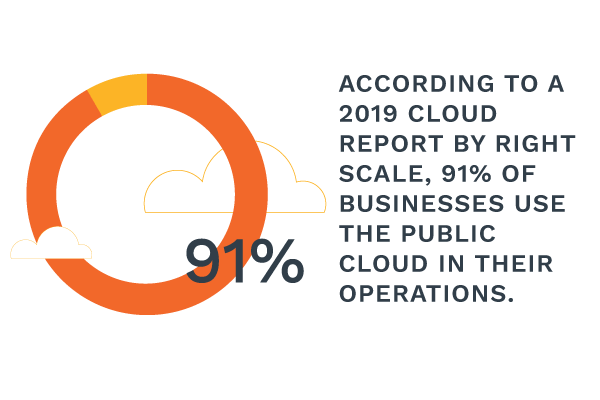
Cloud computing is fast becoming a staple in modern business. In fact, the cloud is so popular that 91% of businesses use it one way or the other. As a leading decision-maker in a growing company, you could be wondering what options you have for deploying your company’s applications and data to the cloud. A quick check will inform you that you have three options: The Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Cloud Service Providers. If you are wondering which one is right for your enterprise, you’re in the right place.
Distinguishing the three cloud options and the best strategies for your firm’s cloud adoption comes with a lot of questions: What’s the right one for your enterprise? Does it have to be just one option? Where does your current cloud plan fall short? If you haven’t adopted the cloud yet, then what’s the first step? These are some of the questions to tackle when coming up with a cloud strategy. By exploring the different features of each option, you’ll be armed with enough information to help you and your IT team make the right decision for your company.
Public Cloud
This is the most common form of cloud computing in use today. With the public cloud, the host is responsible for managing infrastructure and resources, while customers share them for data storage and backup. This means that, as a company that is just getting into cloud computing, the public cloud could be a great place to start and see how it can really benefit you. With the public cloud, you gain access to an enormous pool of resources at practically no startup cost. Public clouds have been used in a wide range of company applications, from CRM software, e-mail, and storage.
Public clouds are offered by providers you know such as Amazon (AWS), Google (Drive), and Microsoft (Dropbox). There are also smaller dedicated providers who offer clouds for specialized applications. With public cloud packages like Amazon’s AWS, you get computing and storage capabilities that allow you to run any software you want on the cloud. The public cloud is highly scalable and affordable, allowing you to seamlessly handle a growing volume of data. You also get to shift the responsibility of managing and maintaining the IT resources to your host, reducing operational expenses.
In modern enterprises, the public cloud can be used for development and testing, in training servers, for one-time big data projects, Websites, Project Management, Customer Relationship Management and company emails. Some companies, such as Netflix and e-Commerce sites, trust the Public Cloud to host their core services.
Advantages of the Public Cloud
Affordable
When you sign up for the public cloud, you won’t incur initial setup costs or outlay. Service providers offer different pricing plans depending on your needs. With the right budget and selection, the public cloud will be a very cost-effective way to access unlimited IT resources.
Simple
With the public cloud, it’s your host’s duty to manage and maintain IT resources. Large service providers also take care of information security and availability. You won’t need to hire an in-house team to handle your firm’s cloud needs.
Reliable
The public cloud comes with highly flexible solutions and pricing structures. The public cloud service providers often have extensive networks of servers, which reduces the likelihood of downtimes and single points of failure. With the public cloud, you are guaranteed full-time availability and a very little chance of data loss.
Scalable
Any time you experience a boom in business, you can quickly expand the capabilities of your cloud-hosted applications by changing the pricing plan. You aren’t bound by hardware and timeline limitations. Additionally, you only pay for the IT resources you utilize, making it a very cost-effective option.
The ability to scale resources in the public cloud also makes it an excellent option for backup and disaster recovery. Access to a near-infinite pool of resources allows you to replicate company data, giving your applications high availability and instant recovery in case of a breach.
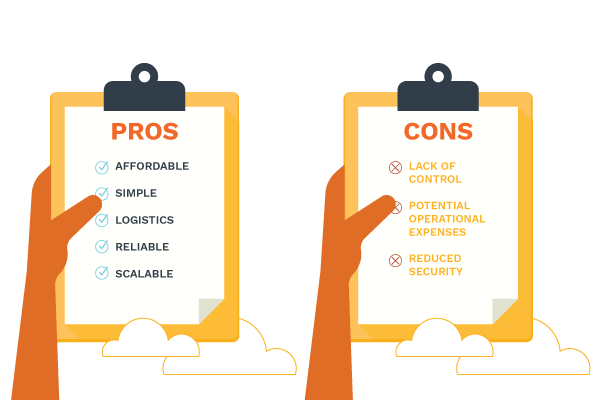
Cons of the Public Cloud
Lack of Control
When you sign up for the public cloud, you don’t own the infrastructure. So, you’re relying on third-party policies and practices to keep your firm’s applications running. This is not a very feasible solution for some mission-critical data and applications.
Potential Operational Expenses
While you don’t pay an upfront deployment fee or maintain the IT infrastructure, you’re required to keep up to date with your billing cycle. The costs add up and may be higher in the long run. If your data and storage needs remain pretty consistent in the long term, the public cloud may not be right for you.
Reduced Security
Since it relies on shared infrastructure, your firm’s information may be vulnerable to unauthorized access. It’s a level of security, though practical, is inferior compared to private and serviced clouds.
Private Cloud
With the Private Cloud, you get a single-tenant cloud environment powered by dedicated hardware. Private clouds are more desirable by larger firms where security is of utmost importance. The private cloud can be configured directly to meet your firm’s security regulations. The private cloud is also an excellent solution if you need your applications and data to be constantly available. With the private cloud, the hardware is entirely dependent on your enterprise needs. With a rise in the adoption of cloud services, about 66% of modern businesses have a cloud center while about 13% use an off-site, third party vendor for their private cloud needs.
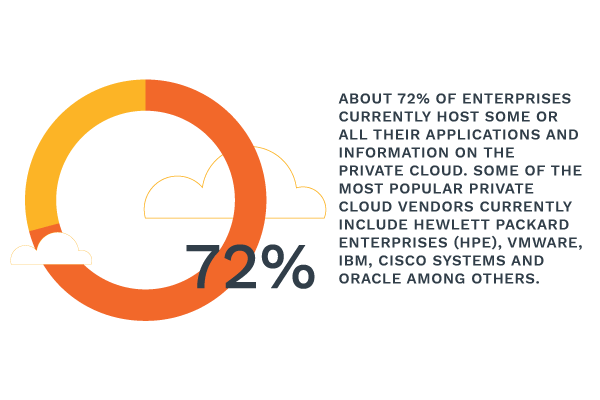
Public cloud providers understand the need to provide top-quality services to their clients. With the Private Cloud, you can be sure of availability, faster data speeds, and a more secure data environment. Even with all these benefits, having the responsibility of security lie entirely on your firm may have its downsides.
Merits of the Private Cloud
Customizable
The Private Cloud is a dedicated solution. You can completely customize your cloud configurations to match the business and technology needs of your company.
Efficiency
Since you’re using dedicated resources, it is easy to assess and analyze your cloud performance. Dedicated hardware also guarantees consistent and fast access speeds. Private clouds generally outperform their public counterparts.
Secure
In a Private Cloud environment, you don’t share resources with other firms. You can tailor your infrastructure’s security to your firm’s needs, ensuring full compliance.

Demerits of a Public Cloud
Costly
When you choose the Private Cloud, you’ll encounter both Capital and Operational expenditure. The upfront costs may not be worth it if you don’t plan to use your cloud strategy in the long term.
Not Scalable
If you want to scale your Private Cloud, you’ll have to plan ahead for investment in increased capacity. You don’t have the option to scale down resources when they are no longer needed. You are generally limited in the increments by which you can scale your cloud environment up or down.
Service Providers
Unlike Private Cloud hosts, Cloud Service Providers add the component of staffing and services to your cloud solution. The providers will offer an assortment of services, ranging from simple assistance with configuration & recovery to full responsibility for applications and storage. These services usually differ depending on pricing arrangements. Cloud service providers offer the best of both worlds, giving you the dedicated service of Private Clouds with the flexibility and scalability of the Public Cloud.
These providers offer computing and cloud services on demand. They often provide highly specialized services, targeted toward certain enterprises. Service Providers include IBM Cloud, Cloud Sigma, Adobe Creative among others. With service providers, you get to choose whether you’ll use the Cloud for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) capabilities.
Here are a few features of Cloud Service Providers:
Assistance
The assistance offered by service providers varies depending on your firm’s cloud needs. This flexible arrangement helps you keep staffing costs low while having peace of mind regarding your data backup and security.
Flexibility
Working with a Cloud Service provider, you’ll get a customized cloud platform. These service providers normally offer an assortment of cloud products and will help create a cloud plan that meets all your business needs.

Security
Just like Private Cloud hosts, Service Providers have advanced data centers with physical and logical security solutions that meet modern regulations and frameworks. You can have peace of mind knowing your data is safe and always available to serve your enterprise needs.
Cost
Cloud Service Providers often cost more than the Private and Public Clouds since you are getting hardware, storage, customized needs, and technical support.
The Public Cloud, Private Cloud, or Cloud Service Providers?
The bottom line is, you need a secure, reliable cloud option. Each of these options has desirable qualities that make it right for specific business needs.
If your business is in need of dynamic scaling capabilities, then the Public Cloud is right for you. Additionally, if your business has project-based IT needs and periodically experiences low demand, you could use the Public Cloud. If you also want a cost-effective backup and recovery solution but lack the finances to set up servers, the public cloud gives you recovery options.
If you’re in a highly regulated industry, then you should consider the Private Cloud. This option is perfect for larger businesses whose activity requires advanced data centers. It is also great if you are in the tech industry where rigorous security and control over infrastructure are desirable since it is robust, quick, and secure.
When going for a Cloud Service Provider, you should first determine your firm’s network, storage, and staffing requirements so you can come up with your desired cloud features and capabilities. This way, you can create a custom solution that addresses your firm’s technology and business needs. For your enterprise, you could take advantage of a Hybrid Cloud that lets you enjoy the benefits of each option.
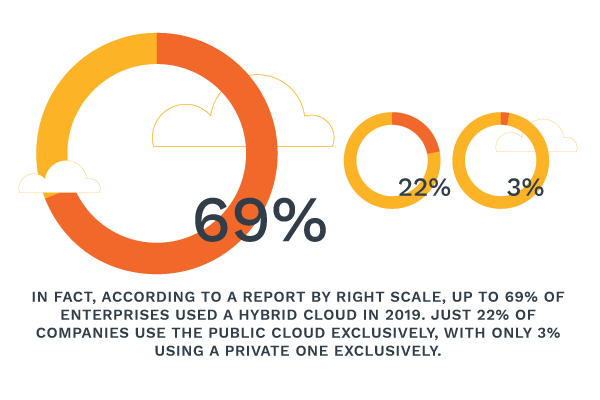
With the hybrid cloud, you can distribute services across both the public and private cloud, then have your host manage some of the functionalities. You can store sensitive data and critical applications on the Private Cloud and host other services on the public infrastructure of your service provider. With assistance, you can always interchange the Private and Public cloud depending on current demands.
Categories: Cloud, Hybrid Cloud