There’s no doubt that cybersecurity is a priority for enterprises today. While the exact future of remote work is still somewhat up in the air, the recent shifts in employee arrangements have opened the door to new (and often unanticipated) threats.
Between 2019 and mid-2020, 16 billion records were exposed, including everything from credit card numbers to medical information.
This article explores how Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools and processes can help your company create a more logical security ecosystem, one that reduces the need for low-level tasks and increases your efficacy against threats of all kinds.
From the benefits of SOAR to challenges to implementation, we cover the basics and what they can mean for your organization. We also see how it compares to the principles of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and how the two can be used to prevent cyberattacks.

What Is SOAR?
SOAR refers to a variety of technologies that help organizations collect data from across the network, including from their security operations team. These tools are there to help people define and drive a logical incident response — one that is standardized across departments.
SOAR involves plenty of security tactics that businesses are likely already utilizing, but the methodology can hone and strengthen them so you’re more prepared for attacks and threats of every variety.
The point of these tools is to tie your response strategy together based on the most likely risks of the individual company. There is no such thing as perfect security, but there is such a thing as throwing up as many layers of defense between your company and its most valuable data.
SOAR is designed to close all the gaps so your security solutions are as strong as they can possibly be. The tactics can reduce the number of false positives, giving your team more time to focus on what matters. It can automate tasks that don’t require human intervention and make for much stronger responses all-around.
We’ll look at how each component of SOAR works to simplify your processes and streamline your security:

Security Orchestration
The increase in complexity and incidence of cybersecurity threats has made traditional incident management strategies obsolete and inefficient.
Security orchestration blends various cybersecurity technologies to work within a single framework. When automated detection isn’t enough, this component requires technical staff (e.g., Information Security analysts, architects, administrators, etc.) to offer support.
This part of SOAR helps businesses improve their response based on current defensive maneuvers and risks. Cybersecurity professionals (Security Analysts and IT Administrators) can replace repetitive, tedious, low-level tasks with automated remediation and response processes.
Automation
This stage of SOAR uses machines to carry out traditional employee tasks. The SOAR framework uses security technologies to enhance low-level operations and integrate them with human decision-making. This speeds up incident investigations and fast-tracks response strategies.
With this step, your cybersecurity team can outline the procedure for:
- Automation
- Decision-making process
- Monitoring & auditing capabilities
- Enforcement actions
To make automation effective, the cybersecurity team must define the response tasks the machines must execute in order. This process creates the security automation playbook.
Response
Response helps cybersecurity staff act on security incidents, collaborate on effective cybersecurity strategies, and have a shared database for strategies used to resolve incidents. Response strategies include:
Alert Prioritization and Processing
The SOAR framework gathers information from security subsystems. Cybersecurity staff then analyses the security data to verify the presence of a threat. In case of a threat, the team investigates other potential risks to prevent further attacks. This triggers the resolution process, which may involve collaboration, coordination, and task administration with the Security Operations Centre.
Threat Intelligence Management
SOAR tools collect all data regarding vulnerability. Cybersecurity staff process the information and turn it into intelligence that forms the basis for future proactive strategies.
Dashboard and Reporting
The final part response will generate reports for all security stakeholders. These stakeholders include the Security Operations Center Managers, the Chief Information Security Officer, Information Security Analysts, and other security experts who are part of the SOAR framework. The dashboard helps staff understand threat intelligence and improve measures based on the information.
How is SOAR Helpful in Improving Cybersecurity at Modern Workplaces?
Cybersecurity challenges are constantly evolving. Malicious threats have grown, both in frequency and sophistication. The advancing risks have not only increased the workload for current employees, it’s made qualified staff hard to come by (particularly when it comes to Security Operation Center personnel).
The SOAR framework allows you to maximize results on security efforts while putting a minimum strain on your resources:
Integrate Security Tools with Threat Intelligence
In most Security Operation Centers, security is sourced from different vendors and the tools seldom work together. Programs and devices that are meant to work with your existing infrastructure often clash more than anyone could have anticipated.
With SOAR, you actually can integrate external threat intelligence with internal security tools. Staff can use these principles to organize and correlate data without the hassle.
Reduce Damage from Attacks
SOAR makes for faster responses and investigations of cybersecurity attacks. SOC staff can start remediation and mitigation sooner — and that’s if they need to get involved at all.
With SOAR, automating your responses will instantly initiate action against the threat. If security staff need to intervene, they’ll already have detailed information about the nature of the attack, and can then act quickly to minimize the damage even more.
Simplify Investigation Workflow
SOAR tools have the capability to investigate low-level security alerts. These tools have been programmed to escalate only those tasks that require actual human intervention.
This way, cybersecurity staff don’t waste company time investigating false cyber threats. Staff can correlate alerts in one location and zero-in on the root cause of system vulnerabilities.
Quick Response to Incidents
Any enterprise is at risk of a security attack. Cybersecurity teams are tasked with the responsibility of identifying these threats, eliminating the attack, and remediating the damage done.
A faster response reduces both the cost and damage incurred in the course of the attack. SOAR tools accelerate this process through the integration of security tools. Rather than check each of these tools individually, the staff can access all the information in one place, reacting faster to the threats posed.
Eliminate Wasted Time on Manual Processes and False Alarms
In many SOCs, the staff spend a great deal of time on tedious, low-level tasks such as updating firewall rules, decommissioning, adding new users, etc. SOAR tools could potentially automate up to 70% of the staffer's routine work.
SOAR also specifically automates one of the most common problems: false alarms and false positives. The more false alarms, the more time staff spends looking into threats that aren’t real. The more false positives, the more likely it is that staff will ignore the real thing. SOAR tools automate the handling of low-level alarms, reducing the incidence of false positives.
Cost Savings
Since SOAR tools help improve employees’ efficiency and productivity, they offer the benefit of reduced costs and better returns on investment.
What Does SOAR Look Like In Action? Common SOAR Use Cases
Use cases ultimately depend on internal environments, industries, processes, and workflow. However, there are common implementations that can be seen across organizations of all kinds:
- Phishing investigation: 71% of all attacks in 2017 were from phishing. The countless emails received by employees take time to sort through and verify. SOAR automates this task and determines if and when a response is needed. Automation makes it possible to block addresses, check false positives, and quarantine threats.
- Threat intelligence: Lifecycle automation of threat intelligence streamlines the formatting and analysis of your data. It makes it easy for a cybersecurity team to compile and augment your information for a more holistic understanding of the true risks.
- Security incident response: With SOAR, companies can detect, triage, and respond to threats in real-time. This is critical for companies today. In 61% of all breaches in 2017, hackers were able to compromise systems in just minutes. Set up parameters to block malicious IP addresses, terminate user accounts, and isolate compromised endpoints from the network.
- Vulnerability management: SOAR updates security teams on all vulnerabilities in the system based on severity. This invaluable information makes it possible for teams to take immediate action to strengthen the network.
- Ransomware alert: Determine the extent of a ransomware attack and trigger a response and remediation. This use case has become increasingly more of a necessity after the recent surge in ransom requests.
- DoS alert: Denial-of-Service mitigation response can be triggered immediately after receiving a threat. Automation actions may include antivirus scans and notification alerts to end-users.
The Challenges: Why SOAR Can’t Replace Your Staff
With all the talk of automation, you might think that SOAR eliminates the need for a security team. While this might be a tempting thought — particularly with smaller organizations on limited budgets — nothing can replace human intervention.
In fact, this is often the biggest challenge for companies today. SOAR not only requires significant upfront costs, it requires an experienced team that already has an established and documented cybersecurity workflow. If a security team doesn’t understand the metrics they’re using to calibrate risks, they won’t be able to use the platform efficiently.
Another obstacle to SOAR is deployment, particularly in companies with a variety of applications and technologies. While SOAR tools are versatile, there are times when an enterprise won’t be able to support or integrate them. This is another example of where your staff will make a big difference in the implementation of the many tools.
Tips for Implementing SOAR
SOAR tools are designed to integrate with your current systems. Security teams should start with detailed documentation of their workflow though to really understand where the problems are and what can be done to address them. Without this kind of careful preparation, SOAR is unlikely to be effective.
We recommend starting with some common questions to see how to structure your implementation:
- Is your team spending too much time dealing with countless alerts?
- Are alerts being thoroughly assessed on time?
- Would the team be more effective if they could automate certain tasks (e.g., malware incidents, data enrichment, etc.)?
- Are false positives drawing attention away from the real problems?
Implementing SOAR means customizing the tools for your environment and preparing your operations to handle the new workload. It also means taking into account the skill levels of the end users, with some technologies requiring the intervention of highly trained employees and others built for people with all skill levels.
This may require:
- Researching how different user interfaces can encourage non-coders to jump into SOAR solutions
- Double-checking that your current API connectors will accept the pre-written ones of new SOAR tools.
- Ensuring that all connectors will perform the individual actions you need them to.
Before onboarding any new technology, sketch out a diagram on a whiteboard to visualize how everything will work and which tools will interact with one another. SOAR technology can work well with your current infrastructure, but this doesn’t mean you can make assumptions. Some organizations will need to build connectors or adjust interfaces to account for employee needs.
Experts also recommend easing into automation. As noted above, trying to automate an inefficient process will only make those inefficiencies more glaring. Some things just need hands-on intervention from someone who’s seasoned enough to know how to handle it all.
As you can see, the implementation process can be a painstaking one. However, it’s ultimately one that will make your organization better off.
SIEM Security Vs. SOAR Security: Which One Is Better?
You may be wondering if SIEM is better than SOAR when it comes to security. We’ll look at how the two compare and contrast.
What Is the Relationship Between SIEM and SOAR?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems will automate your cybersecurity initiatives, monitor your programs and devices, and identify discrepancies that may indicate a threat. It will trigger security data collection so the SOC team can review the analytics, detect attacks, and respond to threats.
So as you can see, the relationship between SIEM and SOAR is strong. Both strategies are rooted in the many of the same principles and tactics, as they analyze different systems to understand where the risks lie.
What Is the Difference Between SIEM and SOAR?
There are a few key differences between SIEM and SOAR:
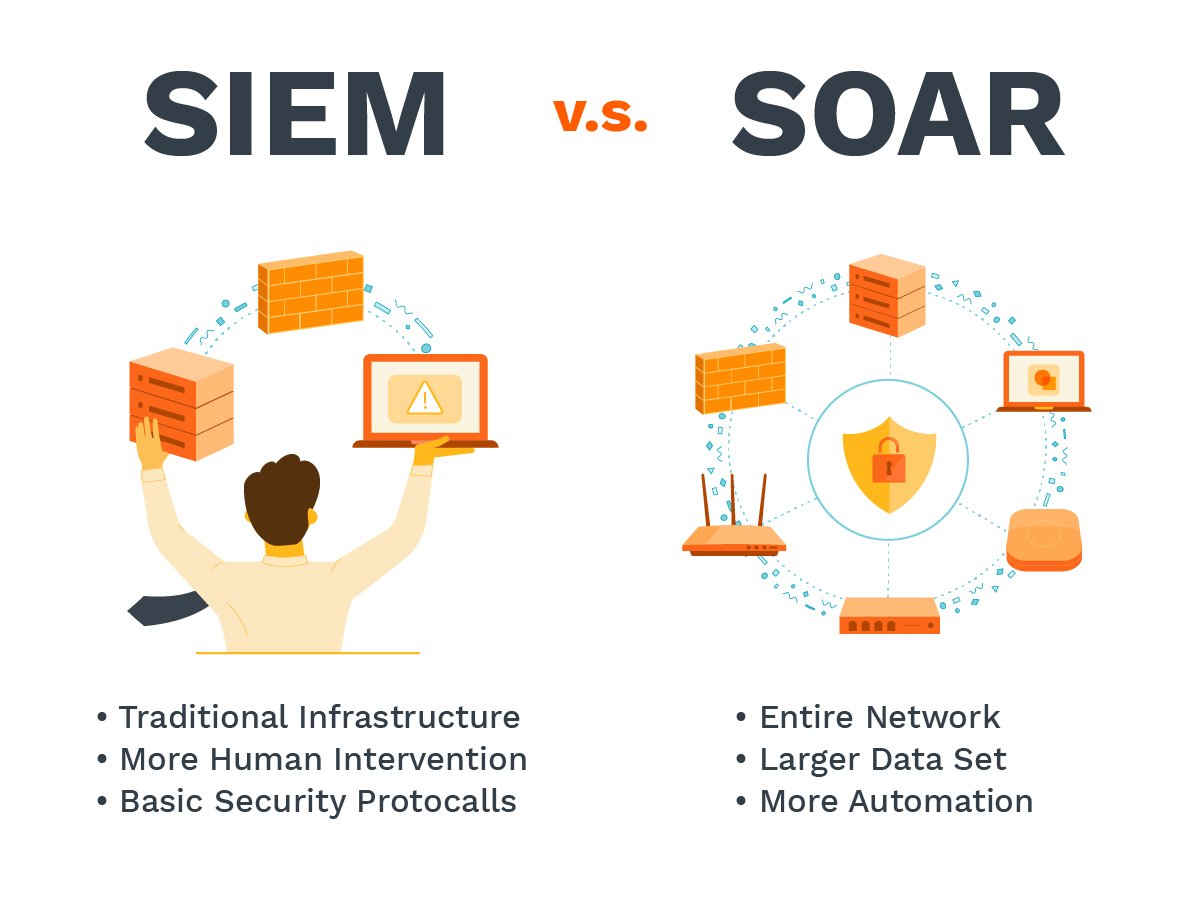
- SIEM is an application that uses log data from different systems to detect the threats and generate basic reports. It’s largely able to work with traditional infrastructure, such as data loss prevention tools, firewalls, and antivirus software. It prompts human interventions through its analysis.
- SOAR helps teams assess the alerts across the entire network, which can make it easier to respond to threats as a whole and track the trends based on a larger set of data. It also automates more tasks rather than requiring human intervention.
- Teams are essentially only looking at a slice of the pie if they rely solely on SIEM. Because SIEM is largely monitoring basic security protocols rather than the whole of the network, it’s unlikely to catch all the vulnerabilities that lie outside the realm of your standard security defenses.
How do SIEM and SOAR work together?
SOAR technically provides the same core functionality as SIEM. However, to really take your cybersecurity to the next level, we recommend using the two together. With SIEM, lower-level threats can be worked with separately, which makes it possible for SOAR infrastructure to specialize in the bigger challenges.
To pass information from the SIEM to the SOAR , we recommend using the messaging system Syslog for recorded events. Your staffers can set parsing rules that convert event logs into readable messages. It reduces the amount of time spent on communicating better policies and makes for more suitable processes within the framework. From here on out, all events can be handled within the SOAR solution.
Wrapping It Up
The evolution of cybersecurity challenges coupled with shifting work patterns has made traditional Security Operations Centers ineffective at best. Most SOCs suffer understaffing as cybersecurity professionals spend huge portions of their workday on routine, low-level tasks. It's why we're seeing more investments in threat intelligence platforms that can handle the load as well as partners who specialize in this subject.
The SOAR platform can help cybersecurity teams improve their awareness and remediation strategies by focusing on high-level decision-making tasks. Additionally, SOAR platforms are able to integrate with your existing Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) systems to provide a multi-faceted approach to information security and threat detection.
Categories: Security, cyber security, Network Security, proactive network security, it security










